Boundary-Aware Distracted Attention Network for Camouflaged Object Detection
|
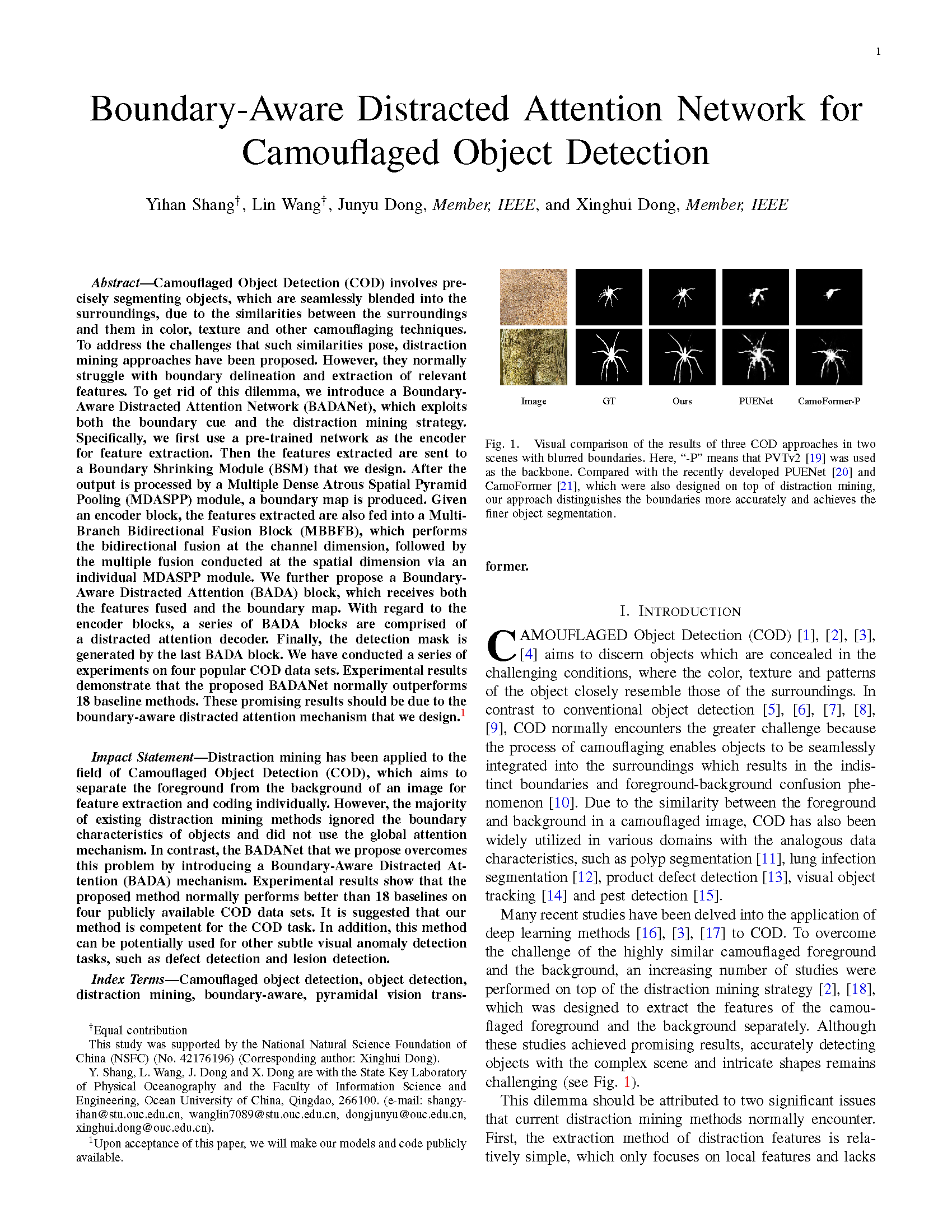
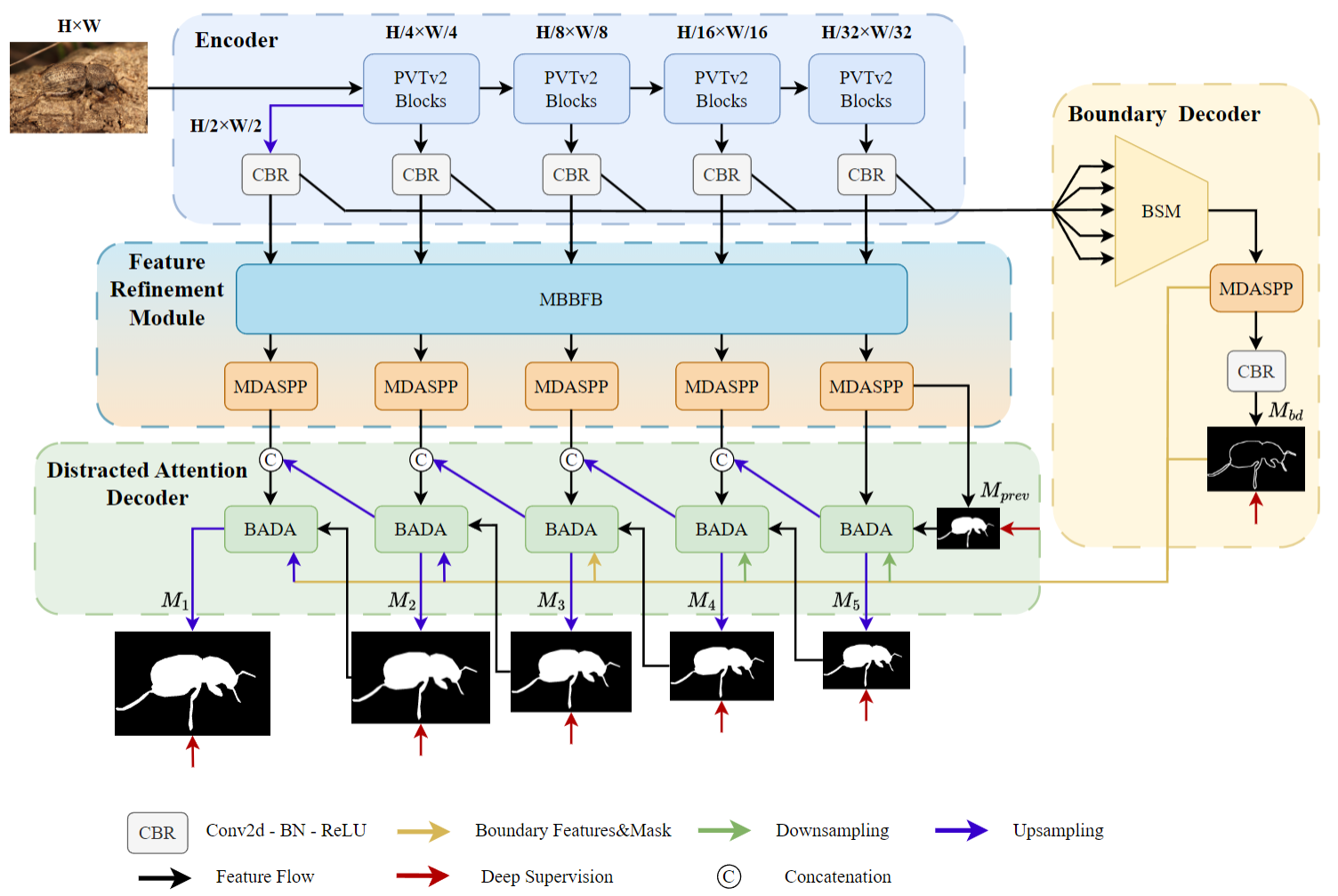
The architecture of the proposed Boundary-Aware Distracted Attention Network for Camouflaged Object Detection (BADANet).
Abstract
Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) involves precisely segmenting objects, which are seamlessly blended
into the surroundings, due to the similarities between the surroundings and them in color, texture and
other camouflaging techniques. To address the challenges that such similarities pose, distraction mining
approaches have been proposed. However, they normally struggle with boundary delineation and extraction
of relevant features. To get rid of this dilemma, we introduce a Boundary-Aware Distracted Attention
Network (BADANet), which exploits both the boundary cue and the distraction mining strategy.
Specifically, we first use a pre-trained network as the encoder for feature extraction. Then the
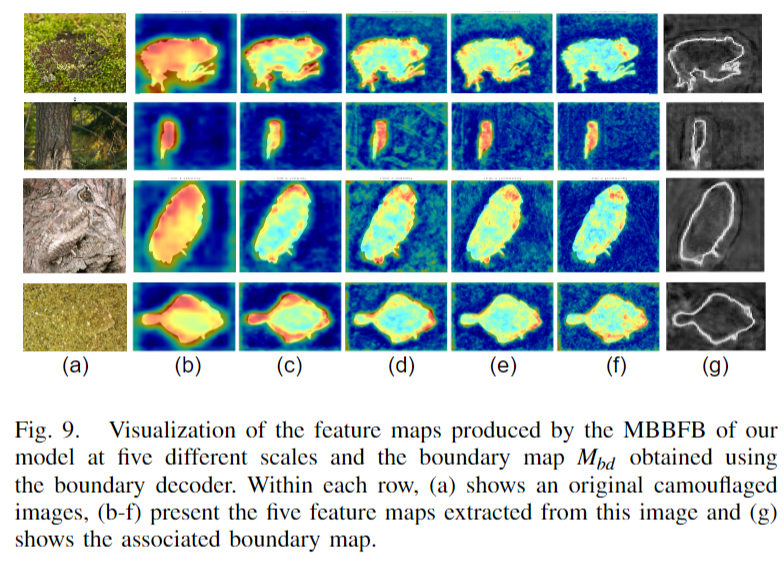
features extracted are sent to a Boundary Shrinking Module (BSM) that we design. After the output is
processed by a Multiple Dense Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (MDASPP) module, a boundary map is
produced. Given an encoder block, the features extracted are also fed into a Multi-Branch Bidirectional
Fusion Block (MBBFB), which performs the bidirectional fusion at the channel dimension, followed by the
multiple fusion conducted at the spatial dimension via an individual MDASPP module.
We further propose a Boundary-Aware Distracted Attention (BADA) block, which receives both the features
fused and the boundary map. With regard to the encoder blocks, a series of BADA blocks are comprised of
a distracted attention decoder. Finally, the detection mask is generated by the last BADA block. We have
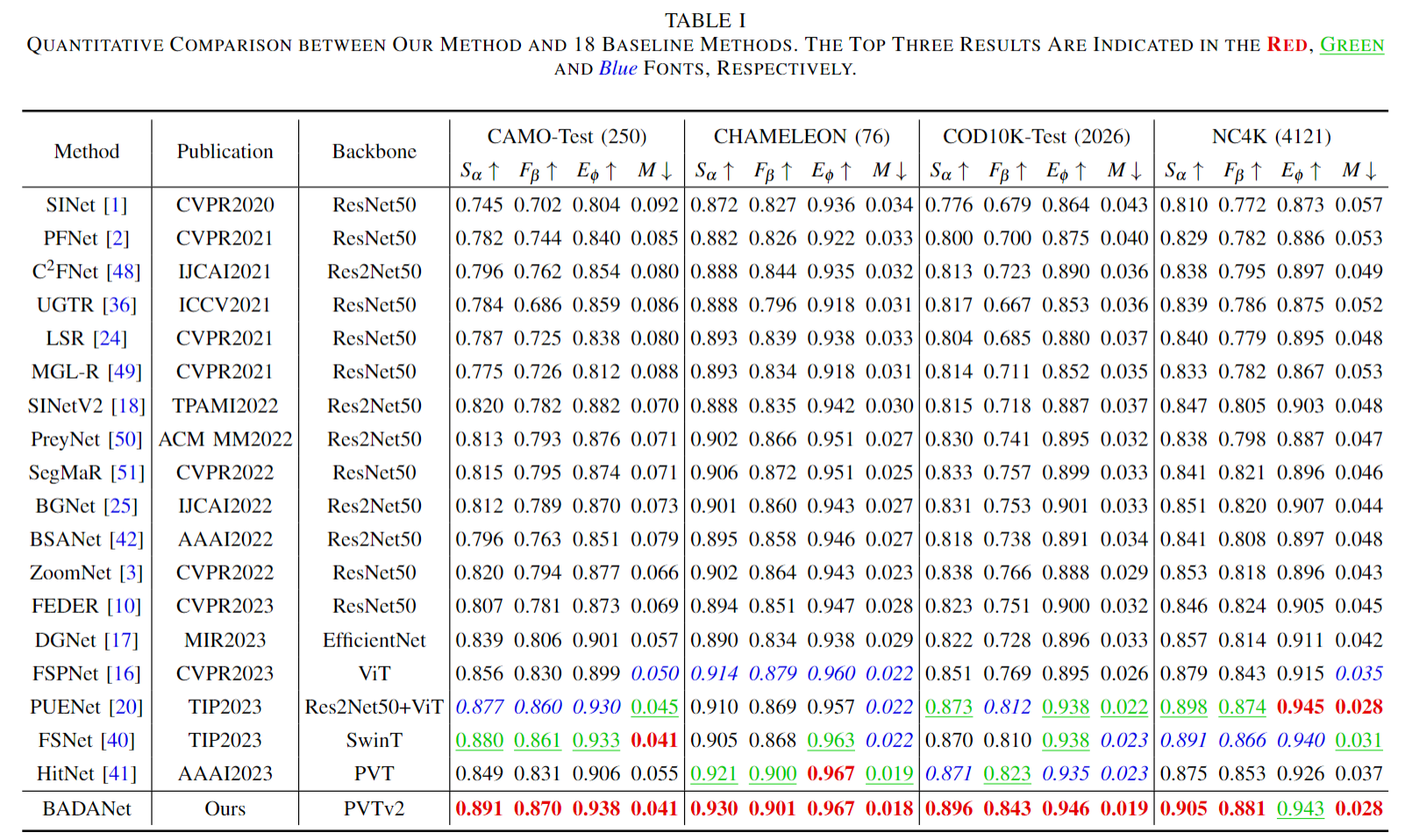
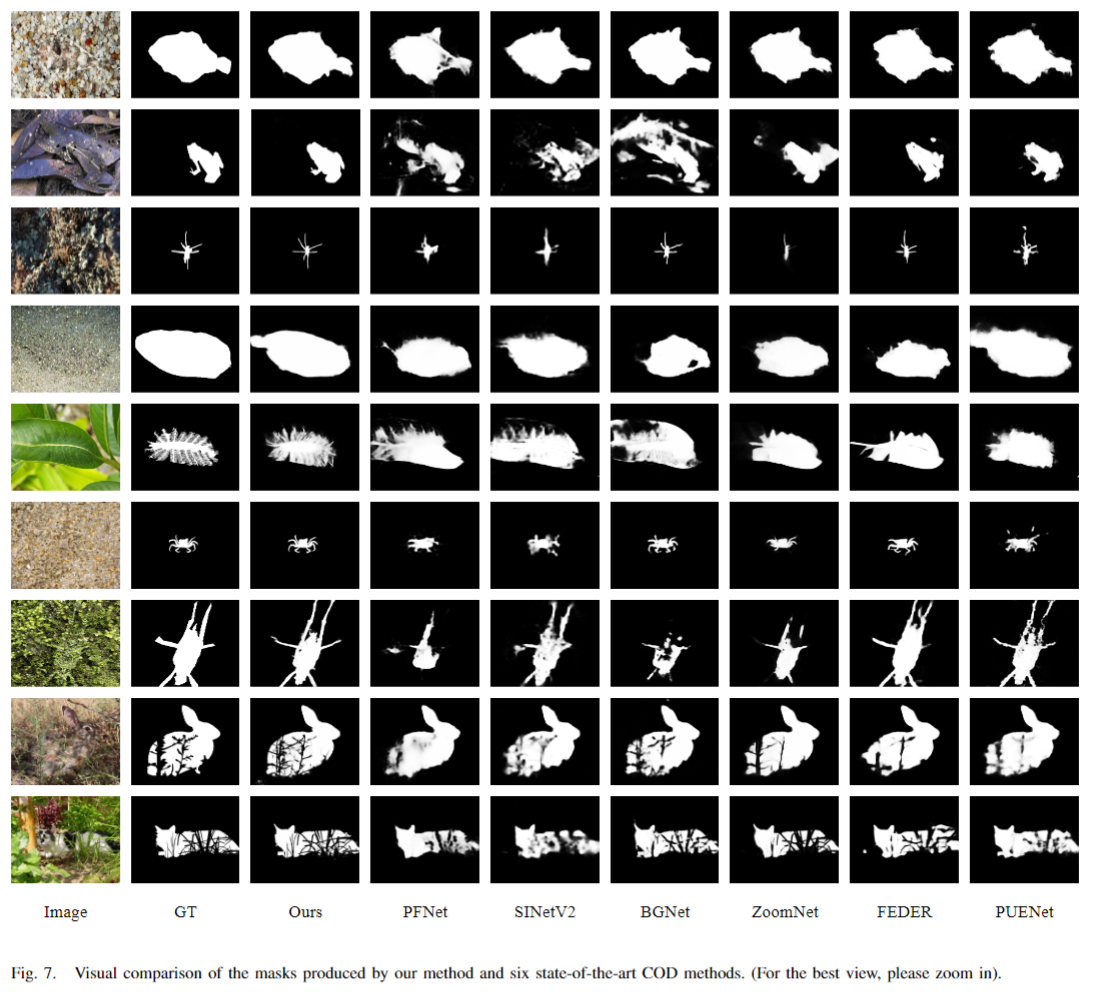
conducted a series of experiments on four popular COD data sets. Experimental results demonstrate that
the proposed BADANet normally outperforms 18 baseline methods. These promising results should be due to
the boundary-aware distracted attention mechanism that we design.
Links
Experimental Results
|

|

|
Citation
@article{shang2026boundary,
title={Boundary-Aware Distracted Attention Network for Camouflaged Object Detection},
author={Shang, Yihan and Wang, Lin and Dong, Junyu and Dong, Xinghui},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence},
year={2026},
publisher={IEEE}
}