Drone-Captured Ship Hull Image Stitching for Inspection: Data Set and Edge-Aware Deep Attention Network
|
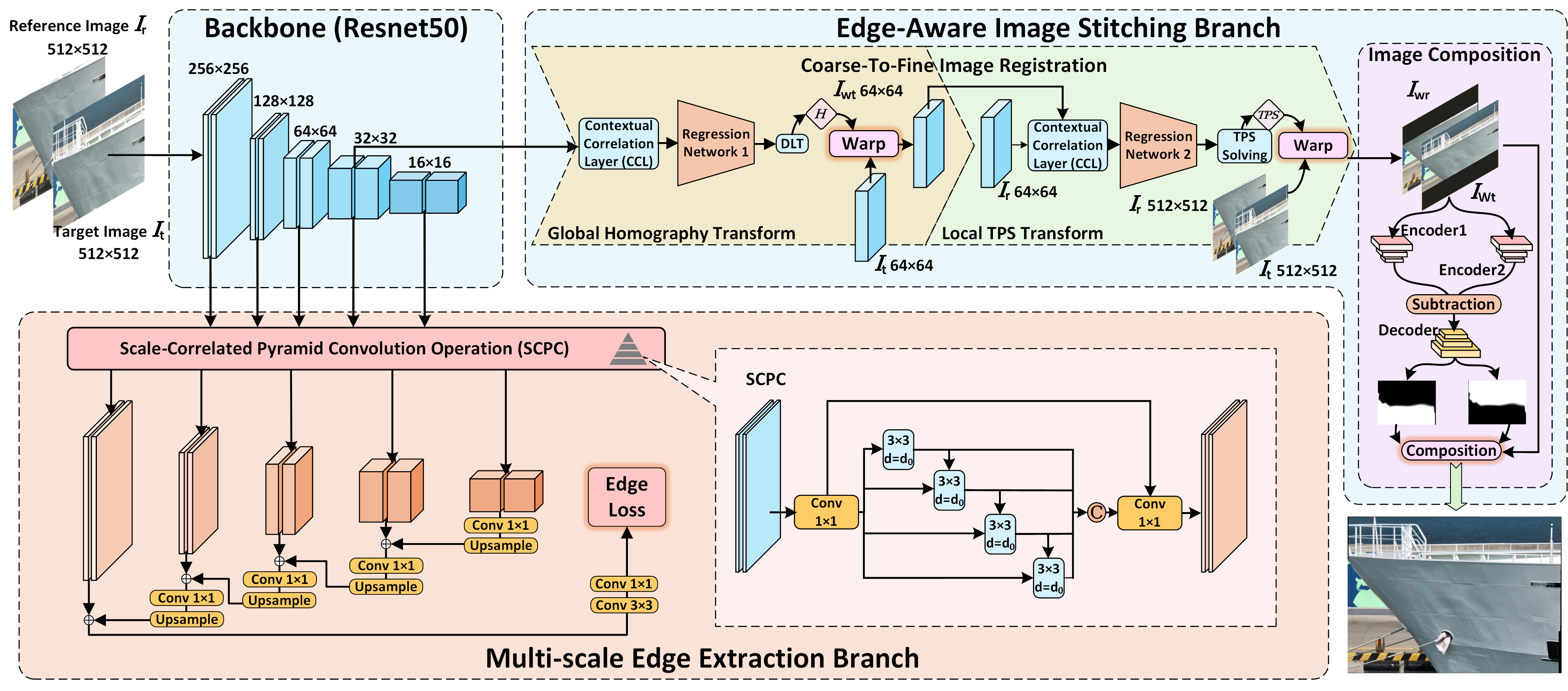
The architecture of the proposed Multi-task Edge-Aware Image Stitching Network (MTEA-StitchNet).
Abstract
Recent applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and machine learning technologies have enabled intelligent inspection of ship surface conditions with high-resolution hull images. Image stitching is a critical step in existing automated hull inspection pipelines. However, hull images are often acquired under challenging conditions, characterized by low texture, limited overlap and large parallax factors that severely compromise stitching accuracy and structural consistency. This issue introduces inevitable challenges to existing hull image stitching methods, leading to reduced performance. Establishing high-quality datasets with realistic hull-surface images and reliable baseline image stitching algorithms is critical for addressing these challenges. This work presents a new benchmark dataset, namely, ShipHull66, consisting of hull images captured under diverse and realistic marine conditions, which enables off-the-shelf training and fine-tuning of image stitching models. Furthermore, we propose a novel Multi-task Edge-Aware Image Stitching Network, i.e., MTEA-StitchNet, which incorporates edge-aware priors and multi-scale pyramid feature matching for effective alignment of geometric structures and coherence of visual information. Compared to state-of-the-art image stitching models on the ShipHull66 dataset, our MTEA-StitchNet has achieved better stitching accuracy, image quality and robustness to complicated environments, as demonstrated by the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) metrics.
Citation
todo